General Information
Oil technology advances due to requirements from engine technology (example: hotter combustion temperatures) or regulatory requirements (example: emissions regulations). There are multiple groups globally that provide standards for oil classifications. Among them are the following.
- American Petroleum Institute (API)
- Association des Constructours Européens d’Automobiles (ACEA)
- Japanese Automobile Manufacturers Association (JAMA)
The API oil category, or any international oil certification, is not sufficient by itself to select the appropriate engine oil for a Cummins® engine. Oils should be selected that meet the appropriate Cummins® Engineering Standard (CES). Table 1 below does provide a comparison between CES and other oil regulatory classifications for reference only.
Note: The CES number should not be considered to be sequential or supersede previous CES numbers unless specifically stated. Higher CES numbers do not necessarily indicate the oil is better than lower CES numbers.
The API requires a set of lab and engine tests that each commercial oil candidate must pass in order to meet the requirements for technology advances. API oil categories define the tests and properties required for a specific oil technology. Examples are below.
- CI-4 category oils were released in 2002 and updated in 2004, coinciding with exhaust gas recirculation technology, to improve soot control and shear stability.
- CJ-4 category oils were released in 2007, coinciding with emissions regulations and ultra low sulfur diesel fuel, to improve compatibility with aftertreatment, wear control, piston deposits, high temperature stability, and soot handling.
- CK-4 oils were released in December 2016 with all the typical viscosity grades of CJ-4 oils. As higher engine temperatures and lower emissions are a continuing trend, improved oils were required. CK-4 has improved oxidation resistance, shear stability, and aeration control. API category CK-4 is backward compatible with API category CJ-4 oil technology.
- FA-4 oils were released in December 2016, primarily as a 10W-30 viscosity grade. FA-4 oils carry the same improved oxidation resistance, shear stability, and aeration control of CK-4 oils. FA-4 oils also reduce greenhouse gas emissions (increased fuel economy, dependent on duty cycle) by lowering high temperature/high shear (HTHS) viscosity. This lower HTHS results in directionally thinner oil films lubricating metal-metal interfaces. API category FA-4 oils are not backward compatible and should only be used when directed by the Lubricating Oil Recommendations and Specifications procedure in Section V of corresponding owners/operation and maintenance manual to use CES 20087 engine oils.
Other global regulatory groups such as the ACEA and JAMA may require additional or different tests.
| Table 1: CES Comparison to Other Oil Regulatory Classifications | ||
| CES | Closest API Category | Closest International Classification |
| Not Approved | CG-4 | ACEA E1 |
| CES 14615 | None | None |
| CES 20074 | None | None |
| CES 20075 | CF-4 | ACEA E2
ACEA E3 |
| CES 20071
CES 20076 CES 20077 |
CH-4 | ACEA E5
JAMA DH-1 |
| CES 20078
CES20088 |
CI-4 | ACEA E7 |
| CES 20081 | CJ-4 | ACEA E9
JAMA DH-2 |
| CES 20085 | None | None |
| CES 20086 | CK-4 | None |
| CES 20087 | FA-4 | None |
Last Modified: 28-Jun-2017
378-004 Determining Proper Engine Oil for Cummins® Engines
General Information
Oils are formulated specifically for different engine technologies. Factors such as fuel type and aftertreatment will influence the type of oil that should be utilized in your engine.
It is critical to make sure the oil being utilized in your Cummins® engine meets the performance requirements set by Cummins Inc. To be sure the proper oil is being utilized for your engine, perform the following steps:
- Identify the appropriate Cummins Engineering Standard (CES) for your engine. See the Owners/Operation and Maintenance Manual, Section V – Maintenance Specifications, and locate the approved CES in procedure 018-003 – Lubricating Oil Recommendations and Specifications. Or for general recommendations, see the following procedures in this manual.
- Use the following procedure for diesel engines.
- Use the following procedure for gas engines.
- Identify the appropriate viscosity grade for your engine. See the Owners/Operation and Maintenance Manual, Section V – Maintenance Specifications, and locate the approved viscosity grade in procedure 018-003 – Lubricating Oil Recommendations and Specifications.
- Identify an oil that meets the correct CES and viscosity grade for your engine. A list of oils that meet the appropriate CES for your engine can be obtained from your local Cummins® distributor.
Do not use an oil that is not registered with the appropriate CES in a Cummins® engine.
Engine oil packaging should contain information on the viscosity grade and CES certification. The CES should be clearly marked with other manufacturer’s certifications. For American Petroleum Institute (API)-approved oils, for example, viscosity grade information can be found in a round service symbol called a “donut”. See Figure 1.
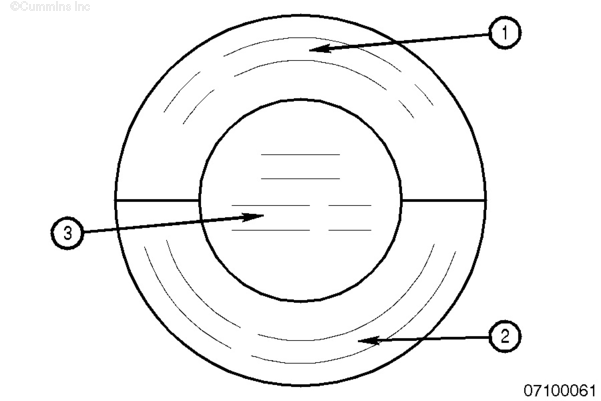
- The upper half of the symbol carries the API oil category (e.g. CK-4) The “C” stands for commercial, but implies use in diesel or natural gas engines. The “K” represents the category as it increases through time. The new fuel economy category (e.g. FA-4) will replace the “C” with an “F”.
- The lower half describes whether the oil has demonstrated energy-conserving or fuel economy properties compared to a reference oil.
The center provides the oil viscosity (e.g. 15W-40).
General Information
Many factors affect the type of engine oil that must be utilized for an engine, such as the use of aftertreatment, exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), and fuel quality.
Multiple oil categories can be allowed for the same diesel engine, however shortened oil drain intervals can be required. Diesel engines equipped with aftertreatment systems require oils with lower sulfated ash content.
Global fuel quality plays a significant role in selecting the appropriate oil. For locations with fuel sulfur > 15 ppm andnot using aftertreatment, do not use oil meeting Cummins® Engineering Standard (CES) 20081, CES 20086, CES 20087, as the starting total base number (TBN) is typically lower and may require reduced oil drain intervals. For fuel sulfur > 15 ppm CES 20078 is recommended.
Requirements
Utilize Table 1 to determine what CES approved oil to use for diesel engines.
Note: CES 20086 is recommended for use anywhere CES 20081 was previously recommended. CES 20086 oil can be used in any diesel engines that are running on ULSD fuel.
| Global CES Oil Recommendation Based on Engine/Aftertreatment Configuration | |||
| CES | Without EGR,
Without Aftertreatment |
With EGR,
Without Aftertreatment |
With Aftertreatment |
| CES 20075 | Not permitted | Not permitted | Not permitted |
| CES 20071
CES 20076 CES 20077 |
Permitted | Reduced Oil
Drain Interval |
Not permitted |
| CES 20078 | Recommended | Recommended | Permitted for some engines2,3 |
| CES 20081 | Permitted1 | Permitted1 | Permitted1 |
| CES 20086 | Recommended1 | Recommended1 | Recommended1 |
| CES 20087 | Not Permitted | Not Permitted | Permitted for some engines1,2 |
| CES 20088 | Permitted for some engines2 | Permitted for some engines2 | Permitted for some engines2,3 |
|
|||
